Three Major Types of Sheet-Metal Processes:
- Cutting
a. Shearing: Cutting operation along a straight line between two cutting edges
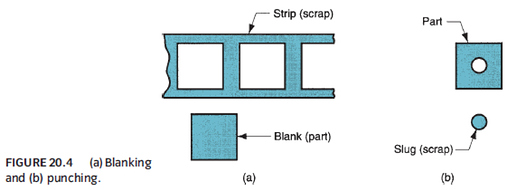
b. Blanking: Cutting operation along closed outline in single step to produce desired part
c. Punching: Cutting operation along closed outline where remaining stock is the part
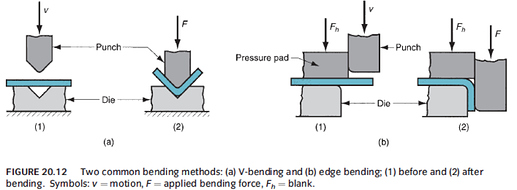
- Bending: Straining of metal around a straight axis to produce plastic deformation
a. Produces little or no change in thickness of sheet metal
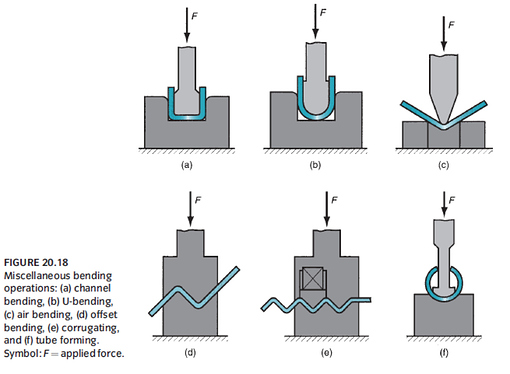
Other Bending/Forming Operations
- Flanging: Straight, stretch, shrink
- Hemming: Bending the edge of the sheet over on itself in more than one bending step
o Improves stiffness and improves appearance - Seaming: Similar to hemming but where two sheet-metal edges are assembled
- Curling: Forms the edges of the part into a roll or curl
o Done for safety, strength, and aesthetics
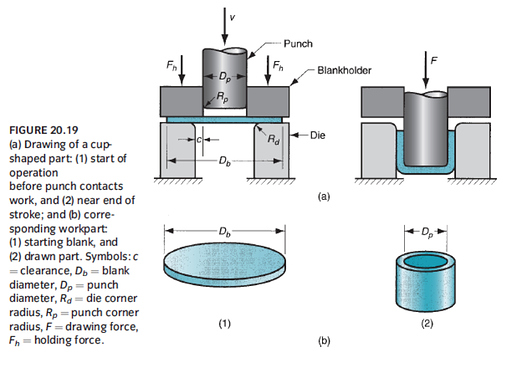
- Drawing: Sheet-metal forming process used to make cup-shaped, box-shaped, or other complex-curved and concave parts
a. Common parts: beverage cans, ammunition shells, sinks, cooking pots, automobile body panels
- If shape change required by the part design is too severe, complete forming of part may require more than one drawing step
o Additional steps called redrawing - Blank holder purpose: Prevents wrinkling of the flange while cup is drawn
o Wrinkling, tearing, earing, surface scratches