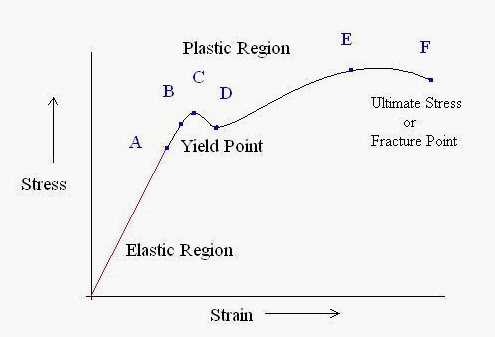
Strain Hardening (also known as cold-working, work hardening): Process of making a metal harder and stronger through plastic deformation.
When a metal is plastically deformed, dislocations move and additional dislocations are generated. This will result in a decrease in the mobility of the dislocations and a strengthening of the material. Occurs at low (relative) temperature.
Occurs between points C and E on the above stress/strain curve.
Think of it as applying further load after reaching the yield point at point B! Strain hardening is used in aluminum-magnesium alloys for beverage cans, and copper-zinc alloys for cartridges.