Thermoforming: Process where a flat thermoplastic sheet is heated and deformed into desired shape
- Applications: Widely used in packing of consumer electronics or fabrication of large items like bathtubs
- Three types: vacuum thermoforming, pressure, thermoforming, mechanical thermoforming
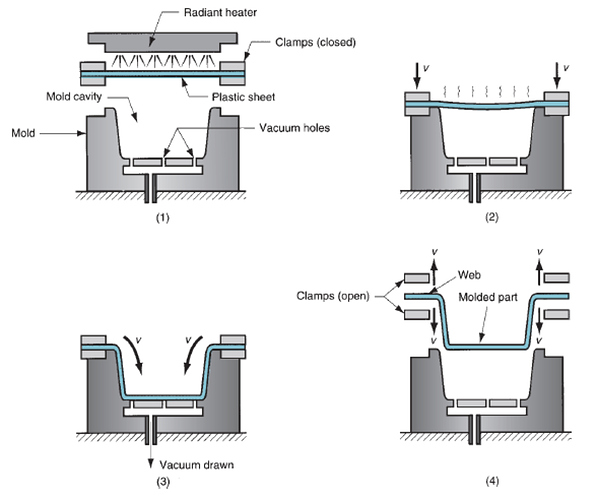
Process: Thermoforming consists of two main steps: heating and forming. Heating is usually accomplished by radiant electric heaters, located on one or both sides of the starting plastic sheet at a distance of roughly 125mm (5in) - Two Types of Mold Cavities: Positive (convex) and Negative (concave)
- Vacuum Thermoforming: Flat plastic sheet is softened by heating, softened sheet placed over concave mold cavity, vacuum draws sheet into cavity, plastic hardens on contact with cold mold surface, and part is removed and trimmed.
a. Negative pressure draws heated sheet into cavity (max pressure = 1 atm)
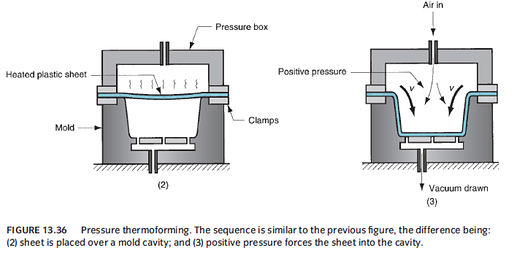
- Pressure Thermoforming (Blow Forming): Uses positive pressure to force the heated plastic into mold cavity
a. Higher pressure can be developed through positive pressure
Common Defects: Thinning of the plastic sheet; significant stretching can occur before stretched to mold contour (Pre-stretching the sheet can help improve thinning distribution)