Describe a CPU heat sink geometry and why it has that geometry. What would you do to improve or decrease the heat transfer.
If you were to crack open any electronic device, you’d typically see this metal block, called a heat sink, mounted on a PCB! Heat sinks exist because all of electronic devices have permissible operating temperature limits at which they’ll operate nominally. Exceeding the temperature margin can lead to device malfunction, and/or physical damage as they overheat.
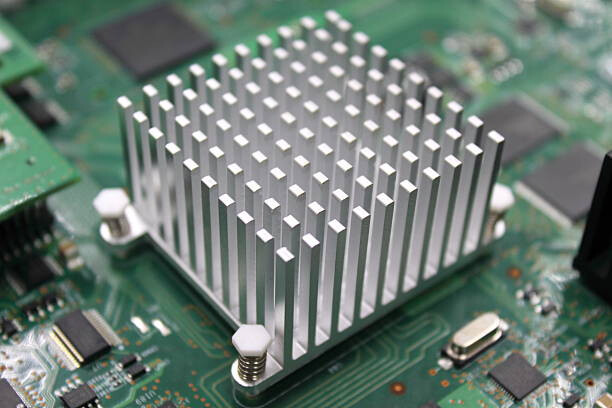

Dissipating heat (Watts) from IC’s (integrated circuits) is one of the largest areas of concern with microprocessor performance, which makes thermal engineering such an exciting field.
TLDR; the better you can cool devices, the better processor performance you can get.
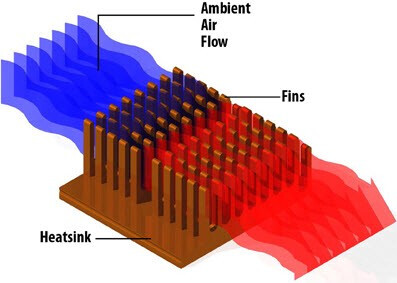
With the heat sink shown above, the primary modes of heat transfer are:
- Heat sink is physically mounted on top of IC (Conduction)
- Fluid (i.e. air) passes over heat sink (Convection)
By having a pin arrangement like shown above, it works to increase the surface area of the component in expediting heat transfer to the surrounding fluid.
Ways in which you can improve heat transfer of a heat sink are:
- Choose a heat sink made of material with high thermal conductivity. The higher the thermal conductivity is, the faster the heat is going to transfer between given two points. Copper can be selected for example instead of aluminum.
- Use thermal glue/paste between heat sink and IC. Thermal glue is a thermally conductive adhesive you can use instead of mounting the two dissimilar parts directly.
Generally speaking, you’re always aiming to maximize the thermal conductivity to reach maximum cooling, and anything that uses power will dissipate heat.
Some really great resources linked here: